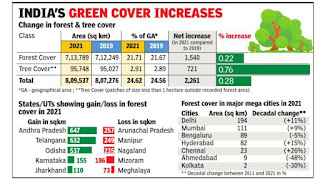
India’s green cover has touched nearly one-fourth of its geographical area with “forests” and “trees outside recorded forest areas” put together seeing an increase of 2,261 sq km (0. 3%) in 2021 compared to the previous assessment in 2019, shows the latest India State of Forest Report.
The total green (forests and trees) cover has now reached 8,09,537 sq km (24. 6% of geographical area), which includes 7,13,789 sq km of forest cover—21. 7% of the area. Overall, forest cover has recorded an increase of 1,540 sq km (0. 2%) while tree cover increased by 721 sq km (0. 8%) in the past two years.
Maharashtra has the fifth largest forest cover in the country, which has increased by 20 sq km. Among cities, Mumbai has 111 sq km under forest cover, the second highest after Delhi. Mumbai has seen a 9% increase in forestcover in the last decade: from 102 sq km, it has gone up to 111 sq km. Maharashtra has shown a 4% increase in mangrove cover, second after Odisha, where the increase is 8%. The increase in mangrove cover in Maharashtra is mainly due to natural regeneration, states the report. Significantly, mangrove cover in Mumbai’s suburbs has gone down by 1sq km, as also in Ratnagiri, Sindhudurg and Thane, but has gone up by 6 sq km in Raigad. The state has 324 sq km of mangrove cover (but no dense mangrove cover), around 90 sq km of moderately dense forest cover and 234 sq km of open mangroves.
The state has 26,866 sq km of tree cover outside the Reserved Forest Area, the highest in the country, followed by Odisha (24,474 sq km) and Karnataka (23,676 sq km). In Trees Outside Forest the spread measured in 2021 was 12,108 sq km. This has in- creased by 1,302 sq km as compared to that in 2019. Maharashtra has the maximum growing stock followed by Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh and Chattisgarh. The maximum number is that of neem and mango in rural areas and coconut and mango in urban areas. These are the most common species of planted trees outside forests.
The bamboo cover in the state has reduced by 1,882 sq km, the second highest reduction after Madhya Pradesh. Hacked bamboo clumps were found across 1,475 sq km. The total area under bamboo in the state is 1. 35 million hectares.
The total forest cover in tiger habitats has decreased. But the good news is that the Kanha to Navegaon-NagziraTadoba-Indravati tiger corridor, which passes through Madhya Pradesh, Chattisgarh and Maharashtra, has the largest forest cover (2,012 sq km), followed by Pench-Satpura-Melghat in MP and Maharashtra (1,196 sq km). The Kanha to Navegaoon-Nagzira-Tadoba-Indravati tiger corridor has very dense forests, spread over 858 sq km, which is 43% of its total forest cover. It also has the highest area under Moderately Dense Forest, which is 883 sq km, or 44% of its total forest cover. On the other hand, Pench-Satpura-Melghat has the highest area under open forest, spread over 392 sq km, which is 33% of its forest cover.
The study shows that parts of western Maharashtra show patches that are extremely or highly prone fire zones. In Maharashtra, large, continuous and repeated fires were reported from Gadchiroli district between November 2020 and June 2021. The number of reported fire incidents were 10,577.





No comments:
Post a Comment